BUYER-BACKED SUPPLY CHAIN FINANCE (BSCF)
Buyer-backed supply chain finance (BSCF) is a key contributor to a healthy, agile supply chain and nurtures both the buyer and its suppliers. A custom BSCF Program will influence supplier behavior, drive participation and maximize working capital benefits while supporting suppliers with cash-flow benefits.
As we all know, SMEs have become an important pillar of economic development and social stability of Kenya. However, the shortages of funds have seriously affected their continuous growth and restricted the further development of Kenya’s economy.
One of the main reasons of SME financing problems is that the loan requirements of commercial banks are too rigid. In order to reduce the credit risk, Kenya’s commercial banks have established credit rating systems, and only the customers who fall in BBB-A-AAA class are considered investment grade and can have access to new loans.
The banks have also generally raised the minimum capital conditions and loan requirements for their customers particularly in the post COVID 19 period. However, the majority of SMEs find it difficult to meet such high requirements and thus are excluded from the banking credit system.
According to the traditional practices of bank credit, SMEs are considered as high-risk borrowers who need to pay higher costs. SMEs often obtain funds from the banks only through secured loans or mortgages, which have more complicated procedures, shorter terms and higher fees. These factors greatly increase the costs of funds and restrain the financing capacity of SMEs.
Seen from a deep insight, the problems of financing difficulties of SMEs not only affect the SMEs themselves, but also impose a limitation on the entire economic development. Due to large population of SMEs, Kenya is now striving to build significant developments in making the processes involved in taking goods from the raw materials stage, through production to the ultimate delivery to the end-consumer, more efficient.
But while there are proposed initiatives to speed up this physical supply chain, the financial services industry has been criticized for its inability to develop at the same pace. This is the case for supply chains that are buyer-driven (as in large manufacturers) and those that are producer-driven (retail and Agri- industries). However, as the latter tends to be more fragmented and decentralized, there is greater room for improving the financial support to all players in the supply chain.
Making the financial supply chain more efficient means reducing manufacturing costs, business process costs and costs related to logistics. But this can only be achieved with a set of financial solutions that are designed around the whole supply chain.
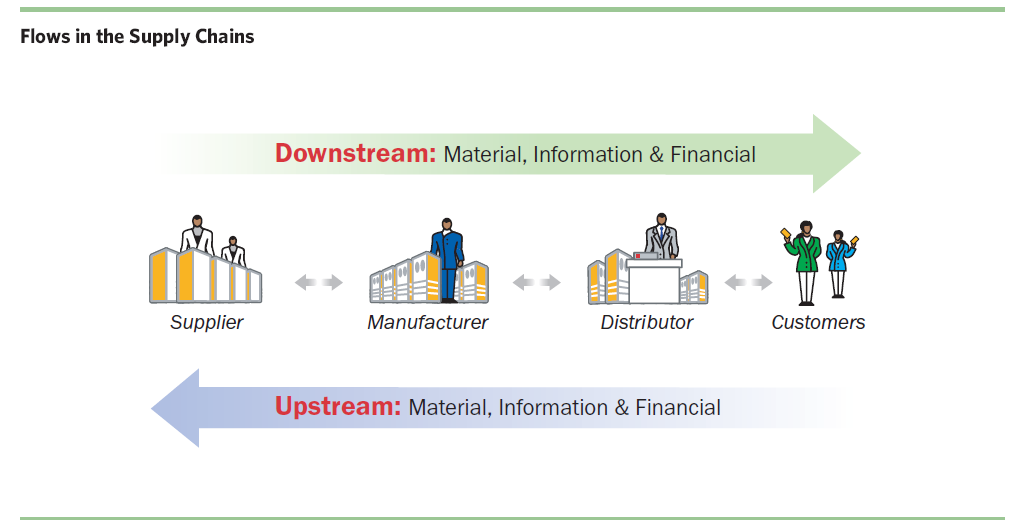
Supply Chain Flows
A supply chain is a network of partners that produces raw materials, sub-assemblies, and finished products, then distributes them via various sales channels to customers. Along this chain, there are three major flows: material flows, information flows, and financial flows.

Efficiencies in the Physical Supply Chain
Therefore, how to change the financing models and reduce the financing costs of entire supply chain has become an important challenge to the new organizational system of production and manufacturing, and thus we need to seek a solution for SME financing from the perspective of the entire supply chain.
Finance Solutions for the Supply Chain
The financial supply chain runs concurrently with the physical supply chain to control the exchange of financial information and payments in the value chain. Efficiency in financial operations is, therefore, equally critical to efficiency in supply chain operations. But how is this to be achieved?
Closer relationships with partner companies and an integrated supply chain are accepted in any enterprise as an effective way to cut costs and increase business agility, yet the financial communications, which form an essential part of the continuum of the business operation are often overlooked. The financial supply chain runs concurrently with the physical supply chain to control the exchange of financial information and payments linking every stage and every partner company in the value chain. Efficiency in financial operations is, therefore, equally critical to efficiency in supply chain operations.
So, what is Buyer-Backed Supply Chain Finance (BSCF) and how does it work in practice?
This is a simple but ingenious process. It allows a large company (Buyer), public or private, with a strong credit rating to pass on this rating – and, therefore, cheaper access to finance – to a smaller company (Supplier- SME), considered a higher risk by lenders.
The system works because it’s designed to be beneficial to everyone. It’s in the interests of buyers that their suppliers get the cash they need to keep going and, of course, that the lender gets their cash back plus profit. It’s been described as a win-win-win scenario and on the face of it, it is.
Here’s usually what happens when provided by the larger company.
A supplier (SME) provides goods and services to the larger company, the buyer. If the supplier SME chooses – perhaps to improve cash flow – the SME can receive payment for an invoice early. The money comes from a lender minus a finance charge and when the invoice is due the money goes to the lender rather than the SME.
Crucially, though, the finance charge is based on the better credit rating of the larger company-the buyer. So, the loan has gone to the smaller supplier-the SME, helping cash flow, the interest has been paid off in full and the risk has been based on the larger company’s i.e. buyer’s superior credit rating.
“Buyer-backed Supply chain finance is clearly an option that all large corporates should consider providing.”
An increasing number of governments, including Kenya are recognizing the fact that by stimulating supplier participation (especially within the Small-Medium Enterprise community) they will also help to stimulate sagging economies.
But why has championing of the Buyer-backed supply chain finance idea carried little if any significant meaning?
May be first we need an efficiency approach, in which improvements to the acquisition process on several fronts such as buyer education, equitable risk sharing and less bureaucratic administration, will remove the barriers to entry into specific markets.
Once the inefficiencies are removed, then Buyer-backed supply chain financing presents a viable option in terms of leveraging a Corporate’s usually stronger credit rating to facilitate faster and/or regular payments on a more favorable cost basis than would normally be available to SME’s through traditional finance programs.
Basic Supply Chain Finance Structuring
The buyer agrees payment terms with its supplier SME;
- The buyer appoints a bank to purchase the supplier’s approved invoices to the buyer immediately, or within days;
- The bank pays the supplier 100% of the approved invoice, less a discount to cover bank service fees and profit;
- The buyer pays the bank the full amount at invoice maturity.
The benefit for the supplier is clear: guaranteed earlier payment, at a modest cost (the discount). The benefits for the buyer are equally clear. First, accelerating cash flows to the supplier, at no cost to the buyer, helps build the financial strength of the supplier. This is especially important because it has become harder for SMEs to borrow; and even when they can borrow, the cost is often much higher than Supply chain finance as pricing for the latter is influenced by the buyer’s higher credit rating.
Second, the supplier’s lower cost of working capital funding is transferred through to the buyer as a benefit in some form, such as a reduction in the cost of goods or services sold. In the private sector, this could also include an agreement to extend payment terms.
Buyer-backed supply chain finance is also known as ‘reverse factoring’, but it is quite different from factoring in several respects. Factoring is a long-established and widely used form of invoice discounting, where the supplier requests the service from the bank, and the bank’s client is the supplier. Supply chain finance turns these relationships around by working with a buyer that is a client of the bank, so that the buyer requests the service from the bank for its suppliers.
This difference in relationships is fundamental as the financing is secured on the higher credit rating of the large corporation that is well-known to the bank, rather than on the supplier and the varied credit ratings of many buyers. Consequently, the financing has a lower cost; the supplier does not have to provide the bank with credit information on itself or its buyer; and the supplier does not need to take out credit insurance in the event the buyer defaults, which is a major benefit at a time in the economic cycle when credit insurance is impossible, or not even available.
Supply Chain Finance and Factoring/Invoice Discounting – What’s the Difference?
The supply chain finance instruments described above sit very comfortably alongside factoring and invoice discounting solutions. Each of these cash flow instruments is different and is individually suited to a particular set of circumstances. One fundamental difference is that, while Buyer-backed supply chain finance benefits from buyer data (i.e. knowledge that invoices to be financed have been approved), factors and invoice discounting providers are generally reliant on information solely from the supplier at the point when funds are advanced.
A Buyer-backed Supply chain finance programme can also be strategically targeted to departments within government in which it might be more immediately suited. More generally, public sector entities can use Supply chain finance to help level the playing field for SME participation in public procurement by offering access to reasonably priced finance in a market where no, or very little, finance may be otherwise available.
As Kenya comes out of recession and the effects of COVID 19, Buyer-backed supply chain finance can be used by public sector bodies to target companies operating in all sectors for better access to working capital to help them invest for growth. Buyer-backed supply chain finance is a good tool in bad times, but it has its uses in good times too.
Why Buyer-backed Supply Chain Financing is poles apart
Buyer-backed supply chain financing is a relatively new concept in the banking industry in Kenya, where a bank examines the company’s supply chain and provides finance to key suppliers and distributors (collectively referred to as ‘channel partners’) for their sales to the company and their purchases from the company, as the case may be.
Supply chain financing differs from traditional bank financing in two significant ways. First, the bank involved does not evaluate the individual channel partners to whom it is providing finance on a stand-alone basis. Rather it evaluates the company in terms of its financial strength and market position, and, more importantly, the effectiveness of its supply chain management practices. If there is demonstrable ‘stickiness’ in the company’s supply chain, the bank would set up facilities for the channel partners without any significant financial assessment of the individual links in the chain. Individual partners are assessed only to establish their position and importance in the overall supply chain and their past trading history with the company.
Defining the parties involved and the business benefits
There are four primary types of players in Buyer-backed supply chain finance. These are the buyer, the supplier, the technology provider, and the financing institution.
Buyers are the primary drivers of Buyer-backed supply chain finance. As the builder of brands, and associated advertising campaigns, they are largely responsible for shaping consumer demand for the products they wish to sell. They’re also the first in the chain to feel the pressure to reduce costs in a market where raw material prices keep rising but consumers want prices to keep falling.
Suppliers need good Buyer-backed supply chain finance the most. As the company that manufacturers (produces) the goods, they not only feel the current increases in raw material, energy, and labor costs the most, but traditionally hurt the most since they need to bear the brunt of the cost and typically go the longest between the initial outlay for raw materials, overhead, and labour and the day they finally get paid for producing the product.
Technology Providers are the enablers of Buyer-backed supply chain finance. They provide the technology that connects all of parties together, and enables the visibility and communication required to support modern supply chain finance strategies.
Financing institutions play the role of lender in Buyer-backed supply chain finance and offer various types of financing, including Global Asset Based Lending (GABL), inventory financing, and insurance, and may offer payables discounting and receivables management services.
Business Benefits
This section discusses the benefits to buyers, suppliers, and both parties.
To Buyers and Suppliers
The great thing about Buyer-backed supply chain finance is that, when done right, it benefits parties all along the supply chain. The benefits described in this section, divided into financial, automation, and general categories, apply to buyers and sellers alike.
Financial
Buyer-backed Supply Chain Finance brings a host of financial benefits to the supply chain. Most of these cannot be obtained through more traditional methods, or at least not to the same degree that Buyer-backed Supply Chain Finance enables them.
Lower End-To-End Costs.
The primary benefit is lower end-to-end supply chain costs. By automating most of the transactions, including approvals and payments when multi-way matching between purchase orders, good receipts, invoices, and contracts lead to non-disputed invoices, supply chain finance removes a lot of manual processing, and its associated administrative overhead and transaction costs from the chain for all affected parties. This results in an instant cost reduction.
Unit Cost Reduction
Proper Buyer-backed Supply Chain Finance, unlike basic sourcing, inventory shifting, or early discounting, actually takes cost out of the chain instead of just squeezing profit margins or shifting cost from a buyer to a supplier.
Shorter Cash-To-Cash Cycles
By automating transactions and enabling third party financing at various points of the supply chain through additional event-based visibility, cash-to-cash cycles can be converted for buyers and suppliers alike. This can substantially reduce costs of financing and, thus, overhead costs.
Increased Cost Transparency
Effective Buyer-backed Supply Chain Finance programs not only point where the costs are, but what they are for. This allows an organization to compare its cost to market averages and increase focus on the areas of the supply chain that are truly ineffective from a cost perspective. No more guessing.
Reduced Cash Flow Uncertainty
With appropriate Supply Chain Finance solutions, buyers know what they owe, to who, when, and for how much as soon as the invoice is created and suppliers know when they are going to be paid, how much, and what opportunities they have for discounted early payments or third party financing and how much it will cost.
Working Capital Optimization
When a holistic Buyer-backed Supply Chain Finance program is put in place, and all areas that impact the supply chain appropriately aligned and connected, for the first time an organization, with the proper tools, can truly be able to optimize its working capital. No more excessive hoarding of cash or borrowing to hedge against the unknown.
Through the enhanced visibility and collaboration that results from a sound Buyer-backed supply chain finance program, CFOs will have direct knowledge of sourcing strategies, payment terms, seasonal variations, and transport methods and this will allow them to plan cash requirements with greater precision and take advantage of more investment opportunities.
Automation
Buyer-backed Supply Chain Finance brings a host of automation benefits to the supply chain. Although many of these can be obtained through more traditional supply chain technology solutions such as e-Procurement, e-Payment, and inventory management, the benefits are greatly enhanced when these traditional technology solutions are integrated into a Buyer-backed Supply Chain Finance Framework.
Reduced Paper
Automating the processing and payment of purchase orders, goods receipts, and invoices when there are no discrepancies in a multi-way match considerably reduces the amount of paper that must be manually processed.
Minimization of Data Errors
Every time something is manually entered, and re-entered, another opportunity for human error creeps in. Since human error is usually the major cause of discrepancies, that only results in considerable man hours being invested to clear up the confusion, it’s easy to see how improved automation can substantially reduce data errors.
Reduced Transaction Processing Time
Automation allows non-disputed transactions to be processed in a seconds, not minutes, hours, or days.
Faster Dispute Management
Since discrepancies are brought to light faster, as well as their root causes, they can be clarified and resolved much faster using automation-enabled Buyer-backed Supply Chain Finance solutions than they could be resolved using purely manual methods.
Increased Inventory Visibility
Automation, and the increased visibility that it offers, allows you to query where your inventory is at any time. It enables an organization to instantly know when it hits a checkpoint, clears customs, and changes ownership (cross border trade)
General
The increased supply chain visibility enabled by good Buyer-backed Supply Chain Finance solutions lead to more than just the automation and financial benefits discussed in the previous sections. This section overviews some of the additional benefits Buyer-backed Supply Chain Finance solutions enable.
Improved Agility
With an integrated end-to-end Buyer-backed Supply Chain Solution, an organization can more quickly respond to demand changes, transportation delays, production short-falls, and unexpected changes in cash-flow.
Increased Analytics Capability
The additional data made available through end-to-end Buyer-backed Supply Chain Solutions enables additional analytics. This allows for the continual refinement of demand forecasts, inventory optimization, and working capital plans.
Enhanced Productivity
Buyer-backed Supply Chain Finance reduces the amount of time an organization needs to spend on tactical manual processes such as invoice approval, payment, and data collection, and frees up an organization’s resources to spend their time on more strategic activities. This allows for a significant leap in productivity.
Improved Customer Service
Less time on manual transaction processing, better demand forecasting, and improved productivity will allow any organization to make great strides in its customer service.
Improved Supply Chain Reliability
Having timely information on a regular basis naturally leads to improved supply chain reliability. An organization knows where it’s inventory is, what its suppliers are working on, and if they are currently experiencing problems that could lead to a slow down. It even allows parties to work together to detect, and resolve, potential problems before they appear.
To Buyers
In addition to all of the benefits outlined in the previous section, Buyer-backed Supply Chain Finance also brings some specific benefits to buyers that cannot be achieved through more traditional supply chain improvement programs.
Off-Balance Sheet Financing
Knowing precisely where inventory is at any given time allows a buyer to securitize its assets and obtain off-balance sheet financing using a number of different options that might include early receivables programs (where a buyer can ensure early receivable payments to its supplier against non-disputed invoices). This allows it to obtain additional capital at low cost without negatively impacting its balance sheet.
Increased Supplier Interest
A buyer with a strong Buyer-backed supply chain finance program becomes considerably more attractive to a supplier than the average buyer since most suppliers are constantly in a capital crunch in a market where the average buyer is trying to improve their financial position at the supplier’s expense by increasing Days-Payable-Outstanding (DPO) terms.
More Days-Payable-Outstanding flexibility
By enabling a multitude of financing options for it and its suppliers, the buyer has a lot more control over its DPO options and the cost associated with each option.
More Control Over Procure-To-Pay Cycle
An integrated Buyer-backed Supply Chain Finance solution gives the buyer more control over the Procure-to-Pay procedure than a traditional e-Procurement, EIPP (Electronic Invoice Presentation & Payment), or P2P (Procure-To-Pay) solution which does not take the broader financial picture into account.
In addition, properly managed Buyer-backed supply chain finance will help a company treat its payables as an asset. In some cases, this will mean trading on their credit to reduce the amount of cash they need today to pay their suppliers. In others, it might be using a dynamic bid/ask marketplace that offers early payment discounts down to the specific day that the supplier wants to get paid.
To Suppliers
The great thing about Buyer-backed Supply Chain Finance is that, when done properly, it provides as much advantage to the supplier as it does to the buyer, which truly allows costs to be taken out of the chain without unreasonably impacting profit margins or shifting costs to the parties least capable of bearing them.
Below Market Financing Rates
A good BSCF solution, by increasing visibility into supply chain events throughout the chain, gives the supplier the ability to leverage the buyer’s credit rating against their receivables. This is an enormous benefit to a supplier whose normal cost of short-term financing is 20% to 40% when their buyer has a much lower cost of capital, often under 14%.
Reduced Cash Flow Uncertainty
If a supplier does not know that a payment will be late or (later than expected) until the payment fails to materialize on the expected date, the supplier could end up scrambling for cash and be forced to accept very costly short-term capital financing (in the 20% to 40% range). This will ultimately drive up the cost of the products they make by a significant amount. A good BSCF solution allows the supplier to see posted payables, with the payment date, as soon as they are posted.
On-Demand Access to Funding and Financing
A good Buyer-backed Supply Chain Finance Solution will include an on-demand software-as-a-service payment or intermediation platform that will connect all parties, buyers, suppliers, and lenders, together in a manner that will allow suppliers to instantly take available of the low(er)-cost lending options available to them (as enabled or co-negotiated by the buyer) at any time.
More Days-Sales-Outstanding Flexibility
The supplier now has much greater control over its Days-Sales-Outstanding as it can choose to convert receivables from the time the invoice is approved until the maturity date into cash using early payment discounts from the buyer or through low-cost sales of such receivables to third party lenders.
